Using Excel with a Stored Procedure as Data Source
How to use a SQL Server Stored Procedure as the Data Source for an Excel Worksheet
This tutorial explains how to connect to a SQL Server Stored Procedure from Excel and insert the data into a worksheet.
Create the SQL Stored Procedure for Excel
Assuming that we already have created the SQL Server Stored Procedure, here is the sample code using the AdventureWorks database in SQL Server 2008:
CREATE PROCEDURE [Sales].[usp_SalesPerformance]
AS
select SalesPersonID, FirstName +
CASE WHEN Len(IsNull(MiddleName,'')) = 0 THEN '' ELSE MiddleName END + LastName as SalesName, AddressLine1 as Address1,
CASE WHEN IsNull(AddressLine2,'^') = '^' THEN City + ', ' + StateProvinceName + ' ' + PostalCode ELSE AddressLine2 END as Address2,
CASE WHEN IsNull(AddressLine2,'^') <> '^' THEN City + ', ' + StateProvinceName + ' ' + PostalCode ELSE '' END as Address3, CountryRegionName, SalesYTD, Convert(varchar(100),null) as PerformanceRating
INTO #tmp
from Sales.vSalesPerson
Update #tmp
SET PerformanceRating =
CASE WHEN SalesYTD = 0 THEN 'Poor'
WHEN SalesYTD > 0 and SalesYTD < 500000 THEN 'Average'
WHEN SalesYTD >= 500000 and SalesYTD < 1000000 THEN 'Greater Than Average'
WHEN SalesYTD >= 1000000 THEN 'Outstanding'
ELSE '' END
SELECT * FROM #tmp
DROP TABLE #tmp
GO
Insert the Excel VBA Module
Using a little VBA, this data can be used as a data source in Excel much like any Table or View from SQL Server...
Open Excel to create a new workbook and using the keyboard click on ALT + F11 to get to the VBA code. Right click on the VBA Project (Book1) and Insert, Module.
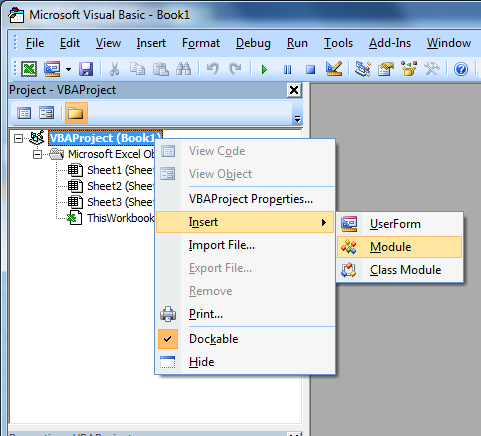
We can now add code to the module for the connection string to the SQL Server and the Stored Procedure name:
Option Explicit
Public Const DB_NAME As String = "AdventureWorks"
Public Const source As String = "usp_SalesPerformance"
Public Const GLOBAL_DB_CXN_STRING = "Provider=MSDataShape;Data Provider=SQLOLEDB;SERVER=#######;DATABASE=" & DB_NAME & ";Integrated Security=SSPI"
Public Sub delSheets()
'delete data worksheets from file
Dim sht As Worksheet
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If sht.Name <> "HEADER" Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets(sht.Name).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End If
Next sht
End Sub
Public Function PopWksht()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim cmd As ADODB.Command
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim rng As Range
Set cmd = New ADODB.Command
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
With cmd
'cmd object to execute stored proc
.CommandType = adCmdStoredProc
.CommandText = source
.CommandTimeout = 300
.ActiveConnection = GLOBAL_DB_CXN_STRING
Set rs = .Execute
End With
Do Until (rs.State = adStateOpen)
Set rs = rs.NextRecordset
Loop
'add worksheet called Data
Set ws = Sheets.Add
ws.Name = "Data"
Sheets("Data").Select
If Not (rs.BOF And rs.EOF) Then
'Copy recordset to the range
rs.MoveLast
rs.MoveFirst
Set rng = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Range("a1")
rng.CopyFromRecordset rs
End If
Set rs = Nothing
Set cmd = Nothing
End Function
We will also need to add the References to the Project so that the code will run:
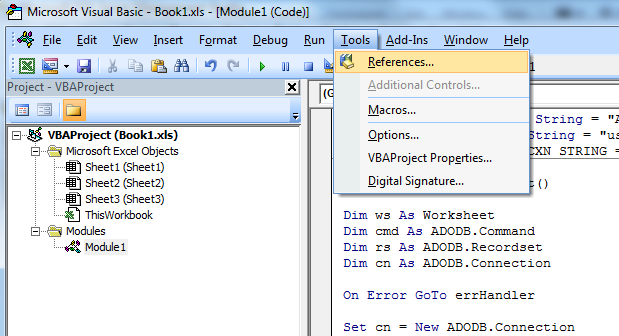
Select Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.x Library and Microsoft ADO Ext. 2.x for DDL and Security and click OK.
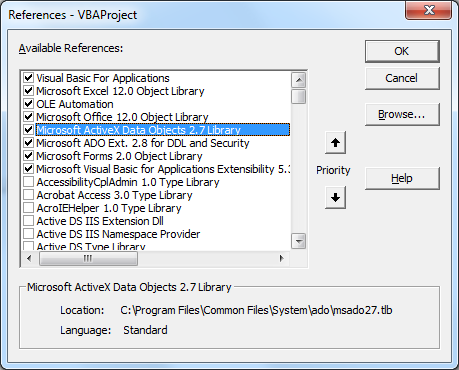
Put the procedures into the ThisWorkbook code under a Public Sub called GenRpt
Public Sub GenRept()
delSheets
PopWksht
End Sub
Run the Macro to get the data into the Worksheet.
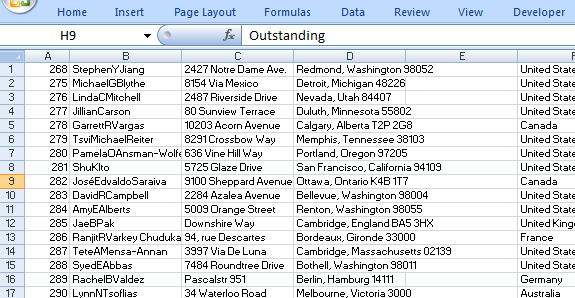
The data does not have any headers nor is it formatted. Please refer to tutorials: Excel Automated Headers and Excel Automated Formatting.
