MS Access Using DAO Recordsets
DAO Recordsets to Modify, Add, and Delete Rows
This article describes how to create code in VBA to utilize the DAO objects in MS Access to automate Insert, Update and Delete processes on a table.
Looping through an MS Access DAO Recordset
The following demonstrates how to open a query as the recordsource and loop through it and print the data to the immediate window.
Create a query with some data. In this case, a table with salespeople and their sales figures will be used.
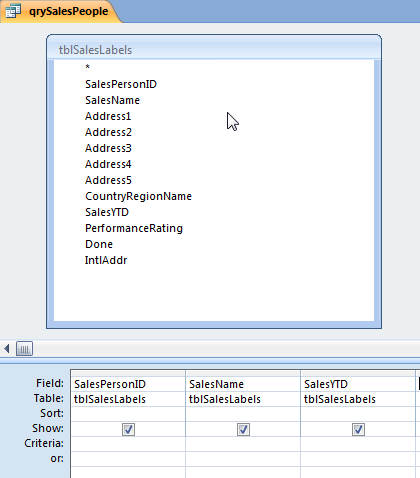
Next, construct code in a VBA Module to generate the recordset with DAO objects and loop through it.
Public Sub daoRecordset()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim qdf As DAO.QueryDef
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Dim strValue As String
Set db = CurrentDb
Set qdf = db.QueryDefs("qrySalesPeople")
Set rs = qdf.OpenRecordset
If Not (rs.EOF And rs.BOF) Then
Do While Not rs.EOF
strValue = rs.Fields(0).Value & ", " & rs.Fields(1).Value & ", " & Format(rs.Fields(2).Value, "Currency")
strValue = Replace(strValue, Chr(13), "")
Debug.Print strValue
rs.MoveNext
Loop
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set qdf = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End If
End Sub
The results from the Immediate Window appear as follows.
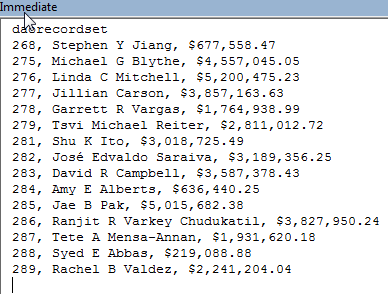
Update Tables with DAO Recordsets
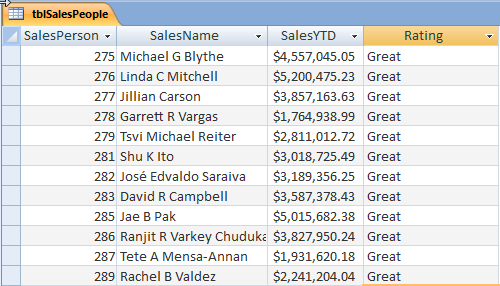
This example uses a table called tblSalesPeople with IDs, Sales Names, SalesYTD, and Rating fields. The Rating field will be updated for each sales person based on their SalesYTD value.
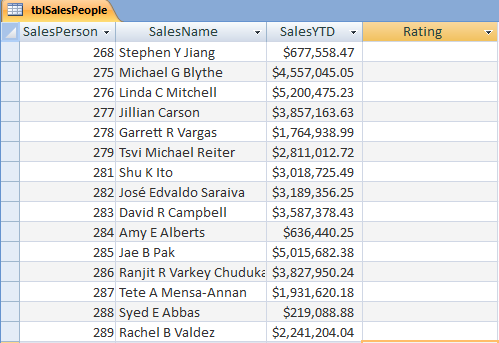
The following code uses the DAO database and Recordset objects to open the table, evaluate the SalesYTD field using a Select Case statement and then updating the Rating field with the value set in the variable strRating.
Public Sub daoUpdateRecordset()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Dim crValue As Currency, strRating As String
'set the DAO database to current Access db
Set db = CurrentDb
'open the table as the recordset
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset("tblSalesPeople", dbOpenTable)
'test to make sure there are rows
If Not (rs.EOF And rs.BOF) Then
'loop through the records
Do While Not rs.EOF
'get the SalesYTD field to evaluate
crValue = rs.Fields(2).Value
'provide a Rating based on the SalesYTD
Select Case (crValue)
Case Is > 1000000
strRating = "Great"
Case Is < 1000000
strRating = "Average"
Case Else
strRating = "None"
End Select
'set the Recordset up for Editing and update the value in the table
rs.Edit
rs.Fields(3).Value = strRating
rs.Update
rs.MoveNext
Loop
'cleanup work
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Verify that the table has been updated with the correct values.
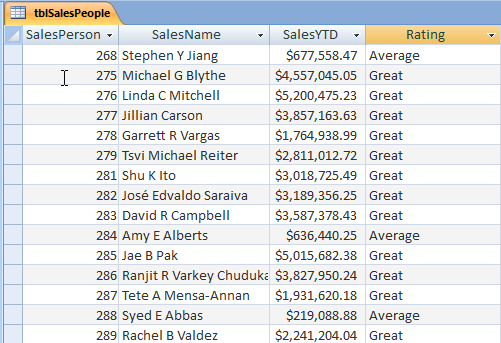
Delete Rows from Tables with DAO Recordsets
This example uses the tblSalesPeople table again and will delete rows based on the sales person's SalesYTD value.
Public Sub daoDeleteRows()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Dim crValue As Currency, strRating As String
'set the DAO database to current Access db
Set db = CurrentDb
'open the table as the recordset
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset("tblSalesPeople", dbOpenTable)
'test to make sure there are rows
If Not (rs.EOF And rs.BOF) Then
'loop through the records
Do While Not rs.EOF
'get the SalesYTD field to evaluate
crValue = rs.Fields(2).Value
'Delete the row based on the SalesYTD
If (crValue < 1000000) Then
rs.Delete
End If
rs.MoveNext
Loop
'cleanup work
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Verify that the rows have been deleted from the table.
Insert Rows Tables with DAO Recordsets
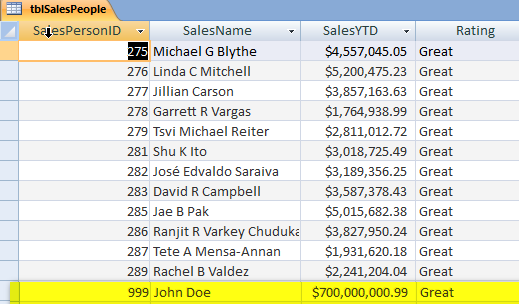
This example uses the tblSalesPeople table again and will add rows using DAO.
Public Sub daoAddRows()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
'set the DAO database to current Access db
Set db = CurrentDb
'open the table as the recordset
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset("tblSalesPeople", dbOpenTable)
'add the row
With rs
.AddNew
!SalesPersonID = 999
!SalesName = "John Doe"
!SalesYTD = 700000000.99
!Rating = "Great"
End With
rs.Update
'cleanup work
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
End Sub
Verify that the row has been added to the database table.
DAO and MS Access VBA can automate processes that need to add, modify or delete rows in tables.
