Using Excel with a Stored Procedure Returning Multiple Data Sources
How to use Excel with a Single Stored Procedure and Multiple Datasets
This tutorial describes how to connect to a SQL Server Stored Procedure that returns multiple data sets into several worksheets.
Create the SQL Server Stored Procedure to Use in Excel
The following stored procedure is based on a view which is inserted into a temp table and then updated. There are 4 sets of data returned by the stored procedure. The goal is to create a worksheet for each of these data sets.
CREATE PROCEDURE [Sales].[usp_SalesPerformance]
AS
SELECT SalesPersonID, FirstName +
CASE WHEN Len(IsNull(MiddleName,'')) = 0 THEN '' ELSE MiddleName END + LastName as SalesName, AddressLine1 as Address1,
CASE WHEN IsNull(AddressLine2,'^') = '^' THEN City + ', ' + StateProvinceName + ' ' + PostalCode ELSE AddressLine2 END as Address2,
CASE WHEN IsNull(AddressLine2,'^') <> '^' THEN City + ', ' + StateProvinceName + ' ' + PostalCode ELSE '' END as Address3, CountryRegionName, SalesYTD, Convert(varchar(100),null) as PerformanceRating
INTO #tmp
from Sales.vSalesPerson
UPDATE #tmp
SET PerformanceRating =
CASE WHEN SalesYTD = 0 THEN 'Poor'
WHEN SalesYTD > 0 and SalesYTD < 500000 THEN 'Average'
WHEN SalesYTD >= 500000 and SalesYTD < 1000000 THEN 'Greater Than Average'
WHEN SalesYTD >= 1000000 THEN 'Outstanding'
ELSE '' END
SELECT * FROM #tmp WHERE PerformanceRating LIKE 'Poor'
SELECT * FROM #tmp WHERE PerformanceRating LIKE 'Average'
SELECT * FROM #tmp WHERE PerformanceRating LIKE 'Greater Than Average'
SELECT * FROM #tmp WHERE PerformanceRating LIKE 'Outstanding'
DROP TABLE #tmp
GO
Adding Excel VBA Code Module
The code below can be added in a new Module to connect to the datasource (Stored Procedure) and produce 4 worksheets using an array. Please note the use of Option Explicit at the top of the code (for the delSheets sub) and also note that the worksheet names in the array are no greater than 30 characters.
The first section declares the constants, such as the Database name, Stored Procedure name, and Connection String.
Option Explicit
Public Const DB_NAME As String = "AdventureWorks"
Public Const source As String = "usp_SalesPerformanceRept"
Public Const GLOBAL_DB_CXN_STRING = "Provider=MSDataShape;Data Provider=SQLOLEDB;SERVER=#######;DATABASE=" & DB_NAME & ";Integrated Security=SSPI"
The next sub in the module deletes all of the worksheets in the file except one called Header. Excel cannot delete all of the worksheets in a file, so Header is just a placeholder to keep the Macro from throwing an error.
Public Sub delSheets()
'delete data worksheets from file
Dim sht As Worksheet
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If sht.Name <> "HEADER" Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets(sht.Name).Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End If
Next sht
End Sub
The next sub in the Module creates and populates the worksheets with ADODB recordsets and uses an Array of strings to name the worksheets as they are created.
Public Function PopWksht()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim cmd As ADODB.Command
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim stClass() As String
Set cmd = New ADODB.Command
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
With cmd
'cmd object to execute stored proc
.CommandType = adCmdStoredProc
.CommandText = source
.CommandTimeout = 300
.ActiveConnection = GLOBAL_DB_CXN_STRING
Set rs = .Execute
End With
ReDim Preserve stClass(4)
stClass(0) = "Poor"
stClass(1) = "Average"
stClass(2) = "Greater Than Average"
stClass(3) = "Outstanding"
Do Until (rs.State = adStateOpen)
Set rs = rs.NextRecordset
Loop
For i = 0 To 3
If i > 0 Then Set rs = rs.NextRecordset
'add worksheets from array
Set ws = Sheets.Add
ws.Name = stClass(i)
Sheets(ws.Name).Select
If Not (rs.BOF And rs.EOF) Then
'Copy recordset to the range
rs.MoveLast
rs.MoveFirst
Set rng = ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Range("a1")
rng.CopyFromRecordset rs
End If
Next i
Set rs = Nothing
Set cmd = Nothing
End Function
Each of the datasets are populated in a separate worksheet and ready for formatting.
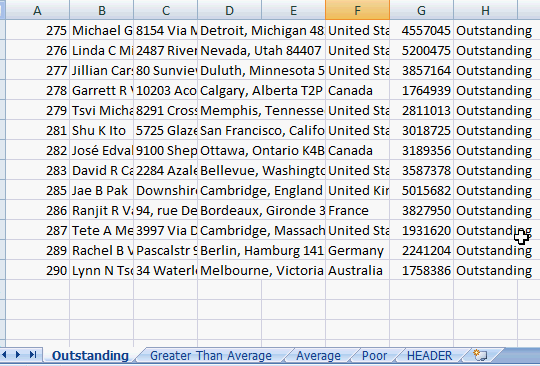
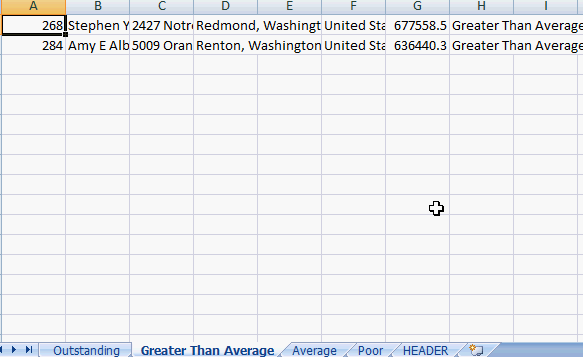
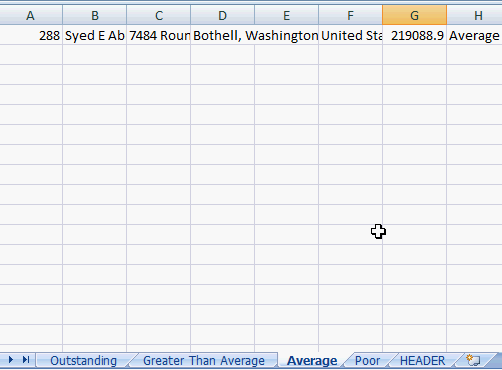
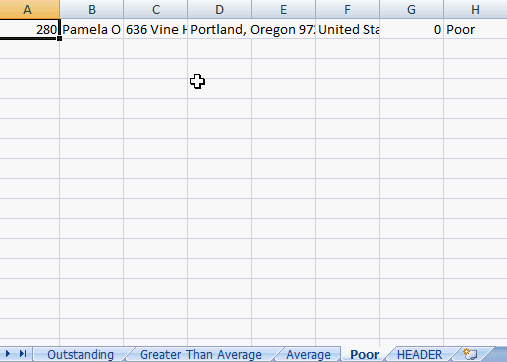
Creating separate worksheets for multiple datasets is easy with ADODB. Please check out Automated Excel Formatting and Automated Excel Headers for additional formatting information.
