MS Word Using 2 Data Sources To Merge into Tables
MS Word Multiple Data Sources Merged Into Single Document
This article describes how to connect to 2 separate MS Access Data Sources (Queries) and import each dataset into rows in their own formatted tables on separate pages in the same Word document. Also included is an addition of a Total Row to a Table in the last row - similar to an Excel worksheet.
Multiple Data Sources in a MS Word
Visual Basic for Applications allows users to connect to more than 1 data source in Word. The Mail Merge functionality in Word only allows a connection to a single data source in a single document. To begin, the first article on this site (MS Word Table Data Merge Rows) provides instructions on how to connect to a single data source in VBA as well as providing VBA Code at the end of the article which may be copied and pasted into a Module in any Word document - just remember to modify the MS Access query and data source to your own local 3 column rowset.
Adding a Second Dataset to Merge into Word
The query for the data to be merged into Word is created in MS Access with a few tables from the AdventureWorks 2014 database via Linked Tables from SQL Server. This query will return the personnel from the first table on page 1 with their email, phone number, and State Code.
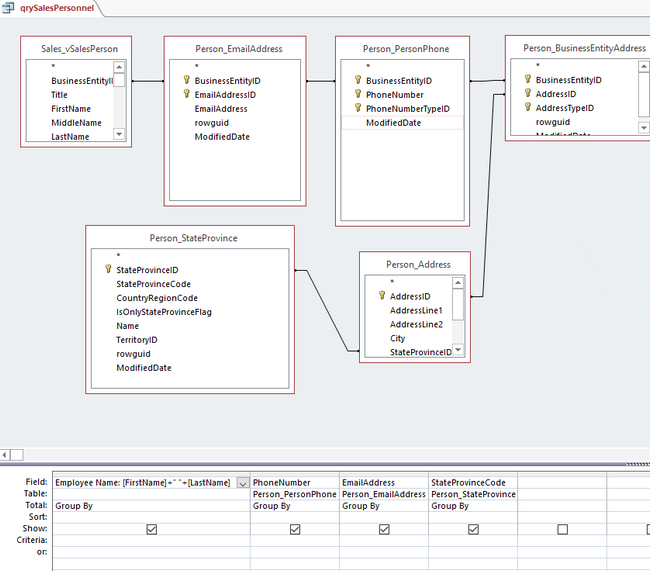
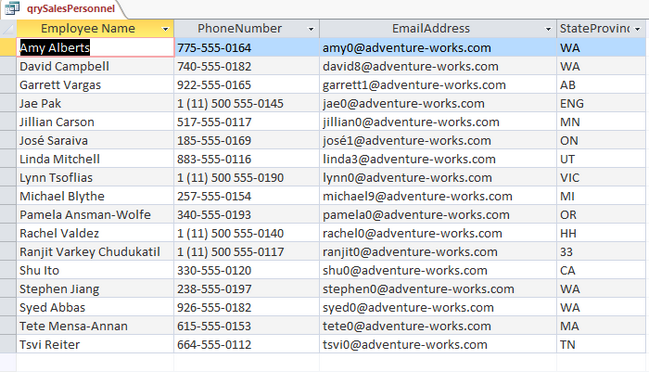
The code is similar to the code from the 1st Sub created, sPrintTable, with a few changes. By copying and pasting the code from Sub sPrintTable into a new Sub (named sPrintTable2), we can save time and make the changes within some existing code. The dataTable name is changed in this new Sub to "qrySalesPersonnel".
sDataSource = "C:\MS Access\Database3.accdb"
sDataTable = "qrySalesPersonnel"
The labelcolumns variable is set to 4 as there are 4 fields being merged into the table.
labelcolumns = 4
The part where the entire contents of the Word document are selected and then Deleted has been Commented Out to prevent execution of the code. It may be removed, if you wish.
'Selection.WholeStory
'Selection.Delete
The value of the Table (t) is changed to 2, as this is the 2nd Table added into the Word document.
'increment of t = 2 to create and populate the 2nd table
t = 2
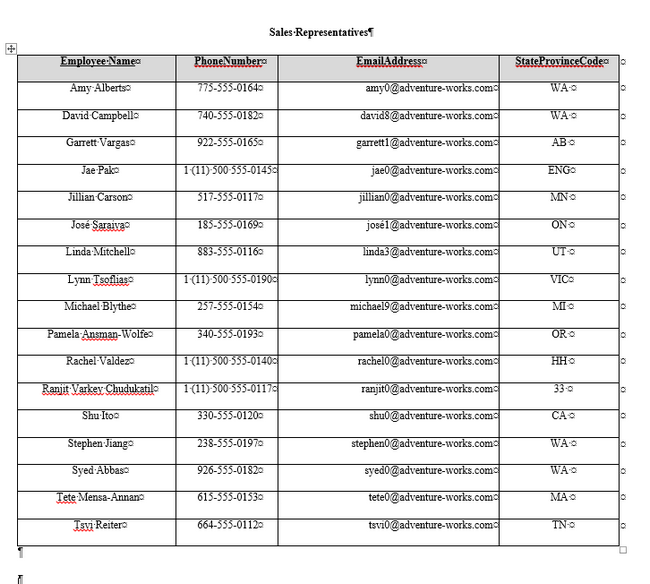
The table will be formatted slightly differently than the first table. The Columns 1 and 3 are a little bigger to accommodate the email and phone numbers returned in the dataset.
ActiveDocument.Tables.Add Range:=Selection.Range, NumRows:=labelrows + 1, NumColumns:= _
labelcolumns, DefaultTableBehavior:=wdWord9TableBehavior, AutoFitBehavior:= _
wdAutoFitFixed
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Columns.PreferredWidth = InchesToPoints(3)
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Columns(1).PreferredWidth = InchesToPoints(10)
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Columns(3).PreferredWidth = InchesToPoints(12)
Executing the code for sPrintTable first, followed by executing the sPrintTable2 code produces 2 tables populated with the data from the 2 different MS Access Queries.
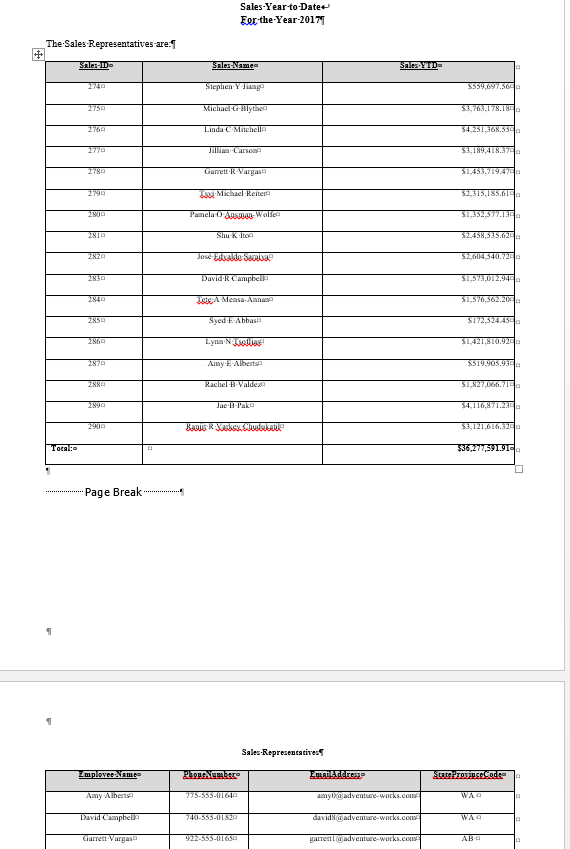
Adding a Total Row To the Merged Data Set
Using the code from the previous Word Page, an additional ADODB recordset is added to the code block.
Dim rsRows As Integer
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset, rsCount As ADODB.Recordset
Dim rsTotSales As ADODB.Recordset 'added Total Field
An additional line of code to Set the new rsTotSales recordset.
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
Set rsCount = New ADODB.Recordset
Set rsTotSales = New ADODB.Recordset 'set new Recordset
Add a new line of code to open the ADODB Recordset and get the Sum of the Sales Year to Date for the additional Row.
'Added SQL code to get Sum of YTD Sales Data
sqlGetTbl = "SELECT SUM([Sales YTD]) as TotSales FROM " & sDataTable
rsTotSales.Open sqlGetTbl, cn, adOpenDynamic, adLockOptimistic
Changed the Row count to + 2 from + 1 to add the extra row for the Total
'changed labelrows + 1 to "+ 2" to add a row to put the Total
If Not rs.EOF Then
ActiveDocument.Tables.Add Range:=Selection.Range, NumRows:=labelrows + 2, NumColumns:= _
labelcolumns, DefaultTableBehavior:=wdWord9TableBehavior, AutoFitBehavior:= _
wdAutoFitFixed
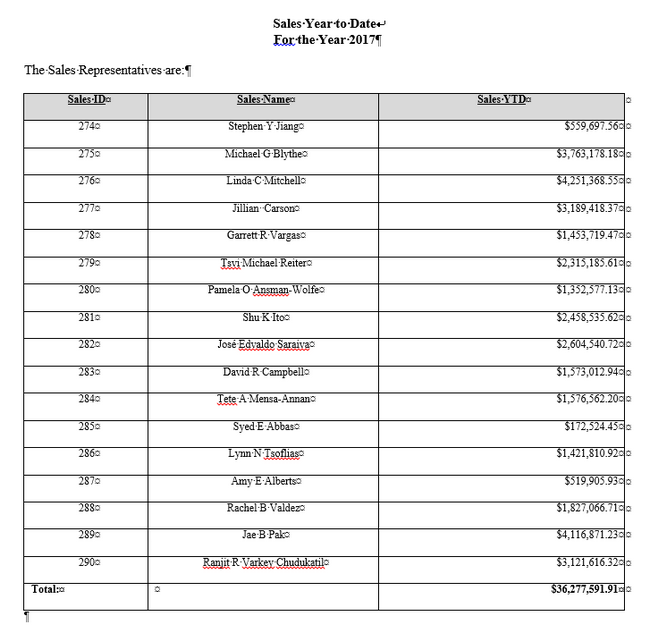
After the loop (at Next j in code), additional data is added to Column 1 and 3 in the last row of the table.
'add total Text to Column 1 and Total Amt to Column 3 in Last Row
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Cell(labelrows + 2, 1).Range.InsertBefore "Total:"
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Cell(labelrows + 2, 1).Range.Font.Bold = True
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Cell(labelrows + 2, 3).Range.InsertBefore Format(rsTotSales.Fields(0),
"$###,#00.00")
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Cell(labelrows + 2, 3).Range.Font.Bold = True
ActiveDocument.Tables(t).Cell(labelrows + 2, 3).Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment =
wdAlignParagraphRight
After closing the Recordset and Connection (rs.Close and cn.Close in the code), an additional page break is added to put the 2nd table on Page 2.
Selection.MoveDown Unit:=wdLine, Count:=labelrows + 2
Selection.TypeParagraph
Selection.InsertBreak Type:=0 'add page break
By running the code using the Immediate Window (or pressing F5) in the VBA Code of the Word document, the table with a Total Row will be created.
You can then rerun the sPrintTable2 code to get the second page with the additional table on it.